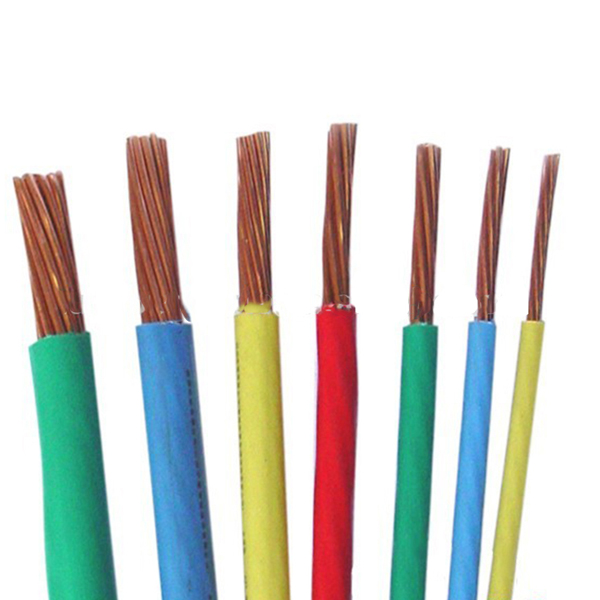
An electrical wire is a type of conductor, which is a material that conducts electricity. Most wires in a home are insulated, meaning they are wrapped in a nonconductive plastic coating. Ground wires are usually solid copper which is either bare (unprotected) or wrapped by an insulated green sheathing.
An electrical wire is a type of conductor, which is a material that conducts electricity. Most wires in a home are insulated, meaning they are wrapped in a nonconductive plastic coating. Ground wires are usually solid copper which is either bare (unprotected) or wrapped by an insulated green sheathing.
Using the right wire type is very important in the electrical project in homes. Knowing how the circuit works and where each wire belongs in the circuit starts by identifying the wire types first in the junction box and where each wire goes. Electrical wiring in homes needs to be updated as most old homes that are built in the 1960s have outdated wiring fittings, not like the new buildings nowadays that have new wiring that is standard to the wiring code.
These are the basic electrical wires for homes:
a. Low-Voltage Wire
Low voltage wire can conduct only 50 volts of electricity or less. These types of wires are mainly used for doorbells, speaker systems e.t.c.
Low voltage wires must not be used on heavy equipment only on low-voltage appliances because they consist of very tiny wires that are different from the standard circuit wires.
Low-voltage wires rarely shock but are best you turn them off before working on them.
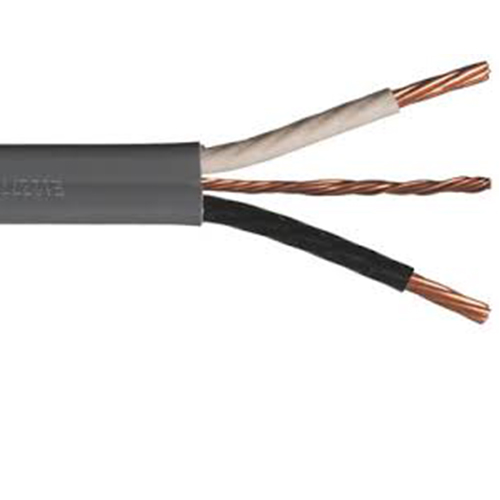
b. None metallic Cable (NM)
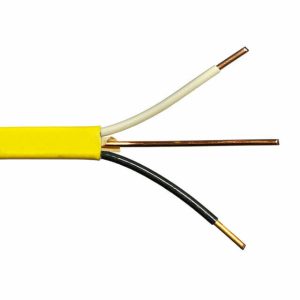
This is a type of wire that is used almost in all outlets and lighting fixtures in homes, it runs through ceilings, walls, and ground cavities of our homes.
How to identify a None Metallic wires (NM) gauge by their color jackets and electricity carrying capacities:
Black sheathing 6-gauge goes with 55-amp circuits
Black sheathing 8-gauge goes with 40-amp circuits
Orange sheathing 10-gauge goes with 30-amp circuits
Yellow sheathing 12-gauge goes with 20-amp circuits
White sheathing 14-gauge goes with 15-amp circuits
c. Thermoplastic Highly heat-resistant Nylon-coated, for added protection (THHN) and Thermoplastic Heat-resistant, Rates for wet locations, Nylon coated, for added protection (THWN) wires.
THWN has a maximum temperature of 90°C in dry and wet locations, whereas THHN wire can only be used in temperatures as high as 75°C in wet locations.
This type of wire is used in basements, garages, and inside homes such as garbage disposal and water heaters.
These wires should never be handled when the circuit is on because it has high voltage running through it.
These wires have a colored sheath that indicates their function in a circuit
Hotwires: Black, red, orange
Neutral wires: White, brown
Ground wires: Green, yellow-green
d. Underground Feeder Cable (UF)
An underground feeder cable is an electrical wire that can be buried directly in the ground, with or without conduit. It is typically used as a feeder or branch circuit cable to extend electrical service underground from the main building to a secondary facility like a lamppost.
UF cable has a strong plastic sheathing surrounding each wire. UF comes with deep gray outer sheathing.
Avoid touching UF wires when the circuit is on because it carries a dangerous amount of voltage.
e. Phone and Data wires
These wires are very low voltage wires used for landline telephones.
Though data wire carries very low voltage anything under 30 voltages is not dangerous.
For more information or assistance during normal business hours, call or e-mail TPS at the phone number above. You can also complete and submit our Service Project Inquiry form.