Power plugs are male connectors that are used to distribute power to electrical devices. They connect to electrical receptacles, wall outlets, or sockets and draw current from these female connectors.
Power plugs provide either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). As electrical connectors, both AC power plugs and DC power plugs are equipped with metal blades or pins that mate with slots or holes. Grounded plugs provide protection from electrical shock.
Different types of power plugs;
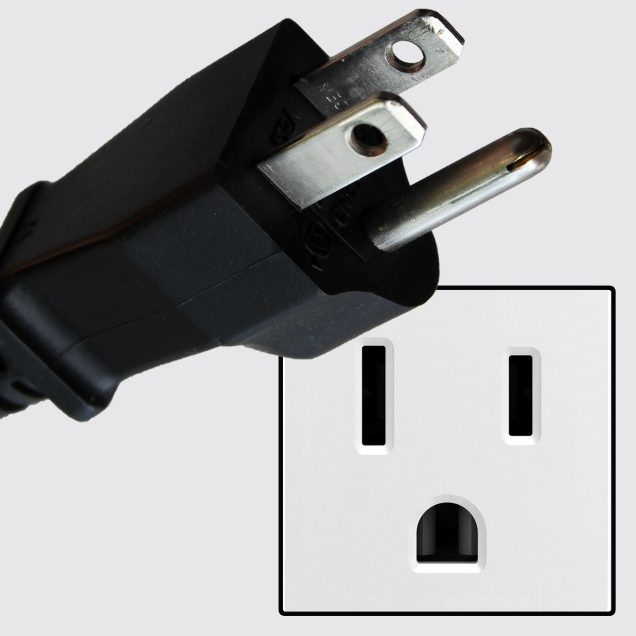
There are two types of domestic wall outlets; the ungrounded type A (NEMA 1-15) and the grounded type B (NEMA 5-15).
TYPE A
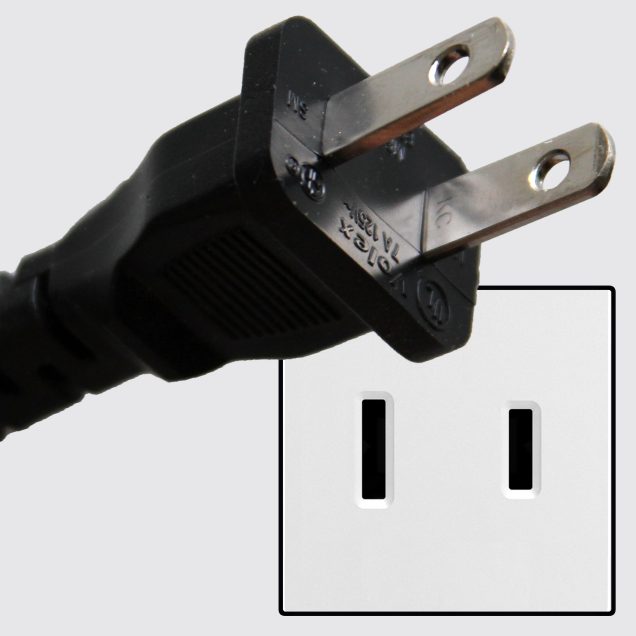
This class II ungrounded plug with two flat parallel prongs is known as NEMA 1-15. The plug has two flat 1.5 mm thick blades, measuring 15.9 – 18.3 mm in length and spaced 12.7 mm apart. Type A plugs are generally polarised and can only be inserted one way because the two blades do not have the same width. The blade connected to neutral is 7.9 mm wide and the hot blade is 6.3 mm wide.
TYPE B
This class I plug is designated as American standard NEMA 5-15. it has two flat 1.5 mm thick blades, spaced 12.7 mm apart, measuring 15.9 – 18.3 mm in length and 6.3 mm in width. It also has a 4.8 mm diameter round or U-shaped earth pin, which is 3.2 mm longer than the two flat blades, so the device is grounded before the power is connected. The center-to-center distance between the grounding pin and the middle of the imaginary line connecting the two power blades is 11.9 mm.
Type A and B plugs have two flat prongs with (often, but not always) a hole near the tip. These holes aren’t there without a reason. If you were to take apart a type A or B socket and look at the contact wipers that the prongs slide into, you would find that in some cases they have bumps on them. These bumps fit into the holes so that the outlet can grip the plug’s prongs more firmly. This prevents the plug from slipping out of the socket due to the weight of the plug and cord. It also improves the contact between the plug and the outlet. Some sockets, however, do not have those bumps but just two spring-action blades that grip the sides of the plug pin, in which case the holes are not necessary.
For more information or assistance during normal business hours, call or e-mail TPS at the phone number above. You can also complete and submit our Service Project Inquiry form.